Ventricular arrhythmias: Hemodynamically stable, sustained monomorphic ventricular tachycardia (off label):
IV:100mg q5min -> 1mg/min.for WPW with Afib. (or even ventricular tachy)
~~!!!
Loading dose: 10 to 17 mg/kg at a rate of 20 to 50 mg/minute or 100 mg every 5 minutes; administer until arrhythmia is controlled, hypotension occurs, or QRS complex widens by 50% of its original width. Although manufacturer's labeling suggests a maximum total loading dose of 1 g, clinical evidence suggests higher weight based loading doses of up to 17 mg/kg may be needed (ACLS [Neumar 2010]; AHA/ACC/HRS [Al-Khatib 2017]). Note: Not recommended for use in ongoing ventricular fibrillation (VF) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VT) due to prolonged administration time and lack of efficacy (AHA 2005; AHA/ACC/HRS [Al-Khatib 2017]).
Maintenance infusion: 1 to 4 mg/minute (ACLS [Neumar 2010]; AHA/ACC/HRS [Al-Khatib 2017]). Manufacturer labeling suggests a maintenance infusion of 2 to 6 mg/minute.
Supraventricular arrhythmias:
Oral [Canadian product]: Sustained release formulation (Procan SR): Maintenance: 50 mg/kg/24 hours given in divided doses every 6 hours.
Suggested Procan SR maintenance dose:
<55 kg: 500 mg every 6 hours
55 to 91 kg: 750 mg every 6 hours
>91 kg: 1 g every 6 hours
Atrial fibrillation (preexcited) (off-label use): IV:
Loading dose: Up to 17 mg/kg at a rate of 20 to 50 mg/minute or 100 mg every 5 minutes; administer until arrhythmia is controlled, hypotension occurs, or QRS complex widens by 50% of its original width. Although manufacturer's labeling suggests a maximum total loading dose of 1 g, clinical evidence suggests higher weight-based loading doses of up to 17 mg/kg may be needed (ACLS [Neumar 2010]).
Maintenance infusion: 1 to 4 mg/minute (ACLS [Neumar 2010]; Hazinski 2015).
Dosing: Renal Impairment: Adult
| Arrhythmia | Treatment options | Contraindicated therapies |
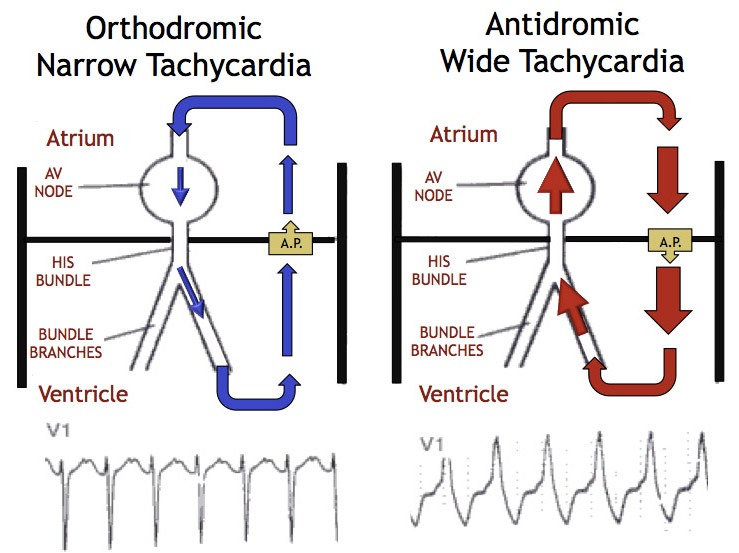
| Orthodromic AV reentrant tachycardia | ||
| Acute termination* |
Unstable patients: Synchronized cardioversion
Stable patients:
| |
| Chronic prevention¶ |
First line: Catheter ablation of the accessory pathway
Second line: Oral flecainide or propafenone in the absence of structural or ischemic heart disease
Third line: Oral IA antiarrhythmic agent OR oral amiodarone | |
| Antidromic AV reentrant tachycardia | ||
| Acute termination* |
Unstable patients: Synchronized cardioversion
Stable patients (if CERTAIN of the diagnosis): Same progression of therapies as acute termination of orthodromic AVRTΔ
Stable patients (if NOT certain of the diagnosis): IV procainamide, synchronized cardioversion if procainamide is ineffective or not availableΔ
| Adenosine, verapamil, diltiazem, beta blockers, digoxin should all be avoided if NOT certain of diagnosis |
| Chronic prevention¶ |
First line: Catheter ablation of the accessory pathway
Second line: Oral flecainide or propafenone in the absence of structural or ischemic heart disease
Other therapies: Oral IA antiarrhythmic agent OR oral amiodarone
|
Digoxin
Beta blockers
Verapamil, diltiazem
|
| Pre-excited atrial fibrillation | ||
| Acute termination* | Unstable patients: Synchronized cardioversion
Stable patients:
|
Amiodarone
Digoxin
Beta blockers
Adenosine
Verapamil, diltiazem
|
| Chronic prevention¶ |
First line: Catheter ablation or the accessory pathway
Second line: Oral flecainide or propafenone in the absence of structural or ischemic heart disease
Third line: Oral IA antiarrhythmic agent OR oral amiodarone
| Oral digoxin |
댓글
댓글 쓰기